Understanding the Momentum strategy in Investing.

Generally momentum in physics is defined as ‘mass in motion’. As per the Newton’s first law of motion that says a body will remain in uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by an external force. But what exactly does “Momentum” means in the world of investing? In this article/blog we will discuss about the in’s and out’s of what is momentum and how it works as an investment strategy.
1) What exactly momentum means in terms of investing?
Momentum refers to the tendency of winning stocks to continue to perform well and losing stocks to perform poorly in the near future. In momentum strategy the stocks are also selected based on their performance in the past with the idea that they will continue to outperform. The investors are attracted to a company whose price is on an upward trajectory thus opening a new way of buying at high and selling higher, instead of the traditional idea of buying at low and selling high, generating higher alpha. Momentum strategies exploit this continuation in return patterns in order to make a profit.
2) How is momentum defined & identified?
Stocks in Momentum could be selected via Time Series Momentum or Relative Strength Momentum which are two distinct measures used to evaluate the performance of stocks.
Time series/relative momentum - Time-series momentum, also known as absolute momentum, assesses a stock's past performance by considering its own returns independently from the returns of other stocks.
Cross sectional momentum - On the other hand, cross-sectional momentum, measures a stock's performance in comparison to other stocks.
3) Why does this strategy works?
1) Behavioural bias
a) Disposition effect - A more behavioural explanation of momentum is based on the disposition-effect. The disposition effect refers to the investor’s willingness to sell “winners” too quickly and to hold “losers” stocks for too long. According to this explanation, investors who suffer from disposition-effect will tend to underreact to news.
b) Anchoring Bias - Alternatively, George & Hwang (2004) explain momentum with an anchoring bias, where investor’s decisions are influenced by or driven towards a certain reference point. The anchor in their study is a stock’s 52 week high price, which most newspapers reporting on the stock market publish. The authors propose that for stocks near their 52-week high, new positive information is at first only partially incorporated into prices because traders are reluctant to cross the anchoring point. Similarly, bad news does not to the extent that would be warranted——-drive down prices of stocks that are already far away from their 52-week high.
2) Information Diffusion
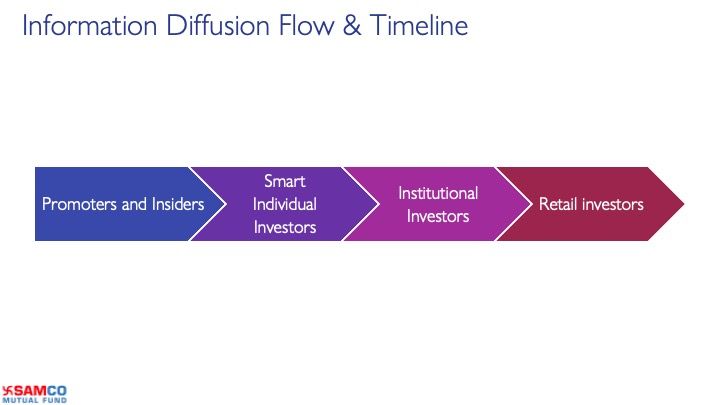
4) Global evidence of the momentum strategy
The existence of momentum is a well-established empirical fact. The return premium is evident in 215+ years (US equity data from 1801-2016), dating back to the Victorian age in UK equity data, in over 20 years of out of sample evidence from its original discovery, in 40 other countries, and in more than a dozen other asset classes. Some of this evidence predates academic research in financial economics, suggesting that the momentum premium has been part of markets since their very existence, well before researchers studied them as a science.
5) Let’s have a look what MSCI has to say about momentum strategy
“MSCI Research shows, on a historical basis, the momentum factor has been one of the strongest generators of excess returns.”
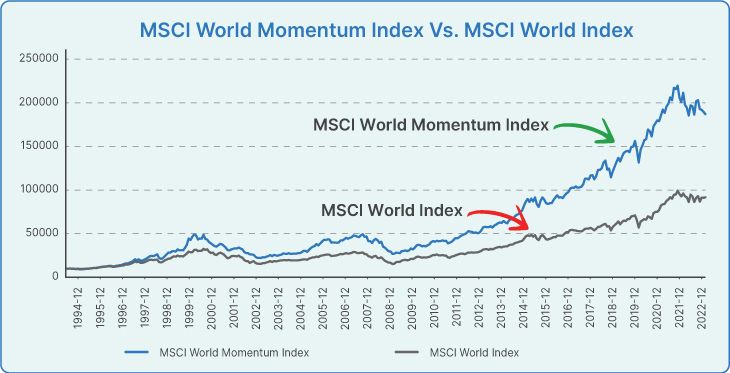
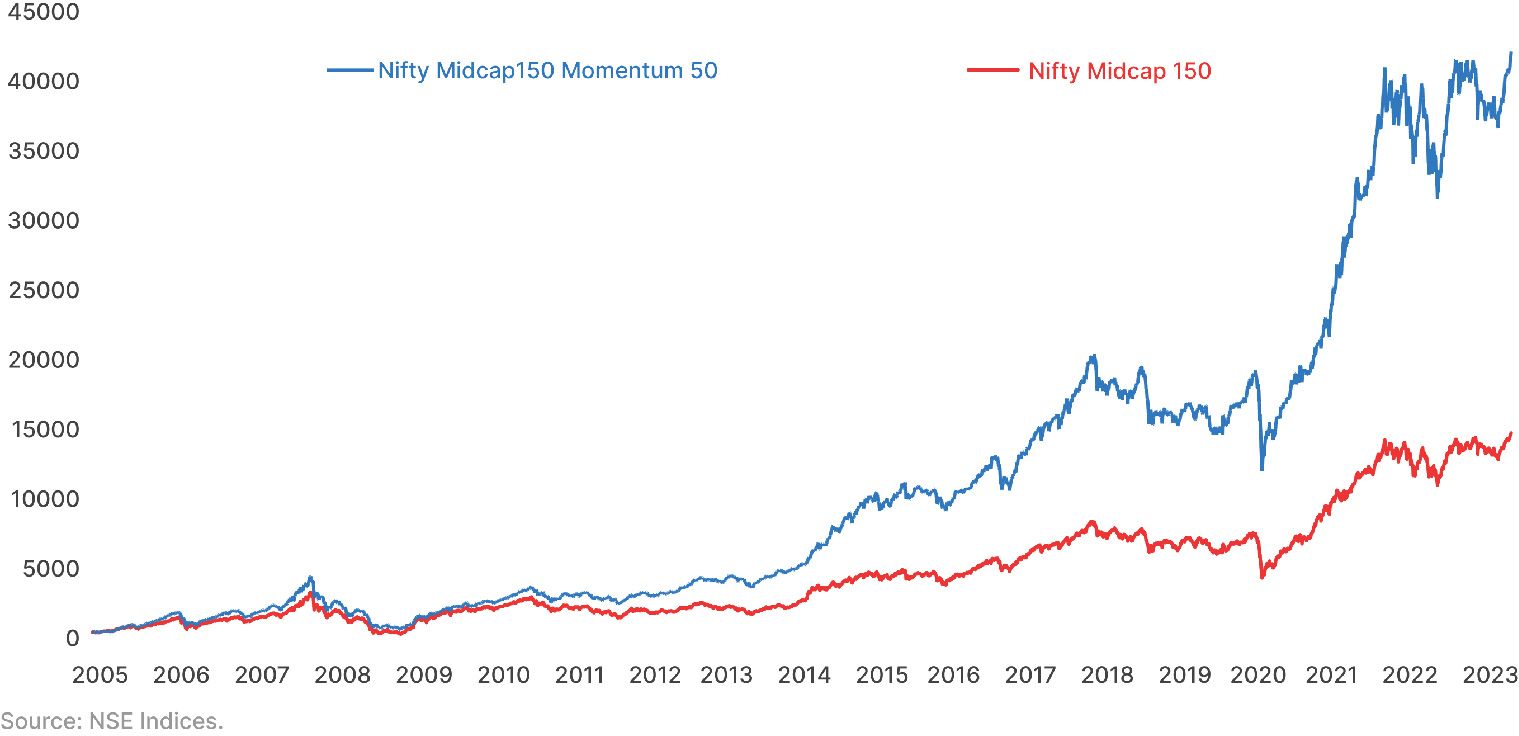
6) Does this strategy works in India?
Yes this strategy works in India as well! Nifty Index has its own Momentum Index which is based on the momentum factor where it churns their portfolio every 6 months according to the momentum characteristics of the stocks.
Nifty India mainly have 2 momentum indices named as:
- Nifty 200 momentum 30 Index
- Nifty Midcap 150 momentum 50 Index
Let’s have a look at the historical performances between Nifty Midcap 150 Momentum 50 Index vs Nifty Midcap 150.
7) There are mainly two forms of momentum investing. Let’s understand what’s the difference between them
- Passive - Passive management emphasises more on the relative method of choosing momentum bearing stocks where it compares the returns relative to its peers.
- Active - Active management uses the relative as well as absolute method of choosing momentum bearing stocks where it compares the relative performance of the stock as well as compares the past performance of its own price in order to analyse that the stock has actually risen in value as well
Let’s understand the advantages of active management over passive:

8) Introducing Samco Active Momentum Fund
India’s 1st active momentum fund that aims to invest in stocks that are showing momentum characteristics using a proprietary momentum-seeking algorithm to generate superior risk adjusted returns.
▶️ NFO Closes on 29th June 2023
🚨 Subscriptions in this scheme shall be accepted during NFO & be restricted post NFO until further notice.
9) How does Samco Mutual Fund defines and identify momentum?
Samco has developed a proprietary momentum-seeking algorithm called the Momentrix Framework which aims to identify momentum in stocks right at the beginning of the catching momentum. This framework is a combination of the momentum definition of index methodologies, well defined momentum characteristics and a distinct pattern identified by the promoter and CIO of the AMC over their investment career. The Momentrix framework is divided in three parts -
- Signal generating engine - Gives us buy, hold and sell signals
- Position Sizing and Risk management Engine - Gives us ideal position size of all buy signals with regards to the risk reward ratio
- Portfolio Management Engine - Give us the model portfolio using signals and their position size, which stock to buy, sell or switch. It also indicates the periods of anti-momentum
10) Data points used by Samco MF to identify momentum characteristics
- Price
- Volume
- Shareholding pattern
- Bulk deals / block data
- Money flows
- Impact cost
- Free float market capitalisation
- F&O data including open interest
- Broader market levels including sectoral indices
11) Understanding the scheme strategy

12) Portfolio construction of this strategy

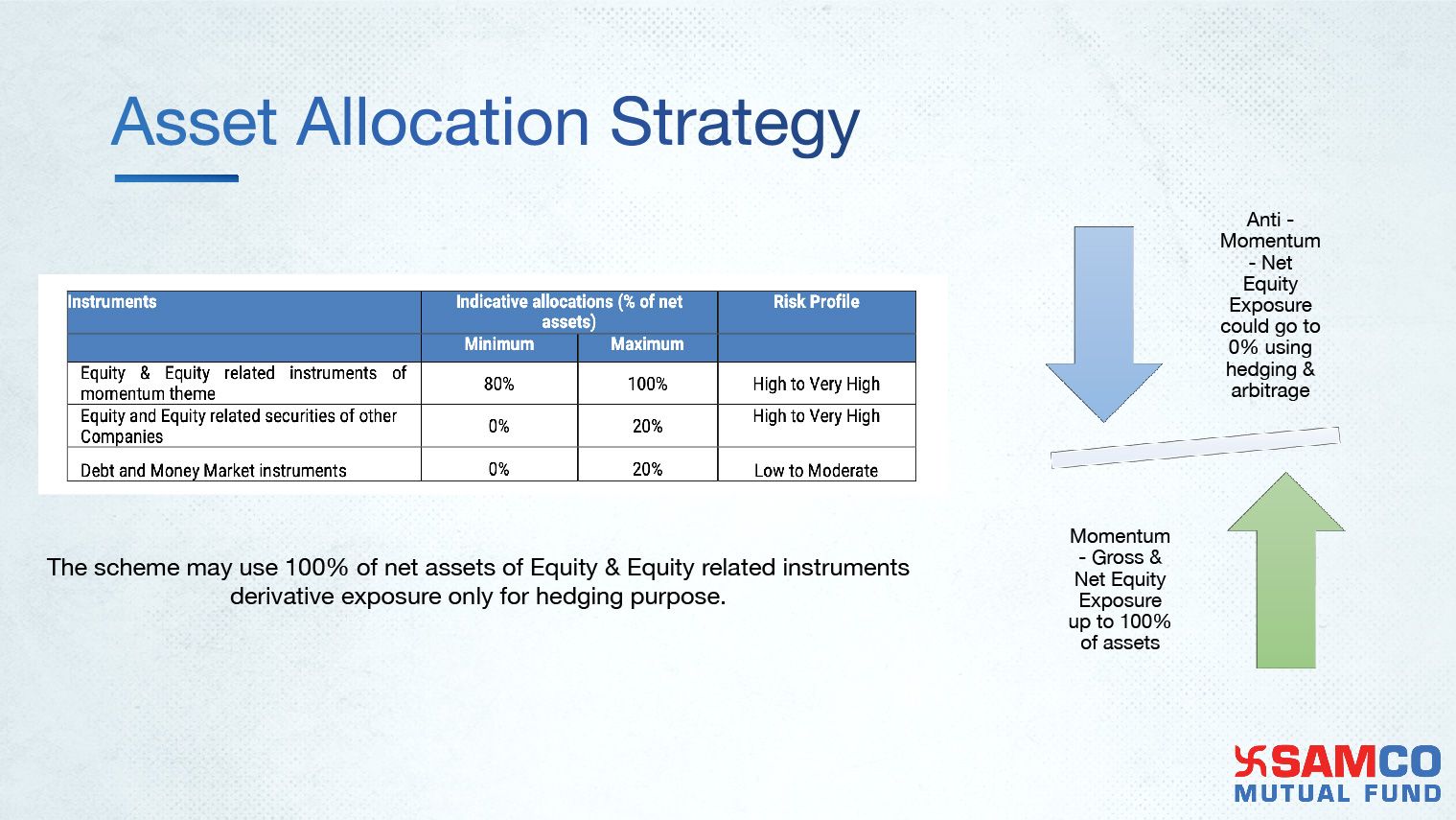
13) Asset Allocation Strategy according to Momentum & Anti-Momentum factors
14) Top 5 reasons to invest in Samco Active Momentum Fund
- India’s first Active momentum fund - Select stocks in form, drops stocks out of form
- Powerful momentum seeking algorithm - Use of technology & big data to mine deep data and generate insights to identify both absolute and relative momentum
- Captures momentum across wide universe - Aims to find hidden opportunities from a wide investible universe of 750 stocks allows identification of opportunities from the time companies including small or micro sized companies.
- Robust risk management - Negative filters to avoid outliers, Hedging during periods of anti-momentum
- Speed & Agility - Rebalancing in real time on loss of form & momentum
15) Scheme Features

Conclusion: As an investment opportunity, Momentum strategy has its own pros and cons. This strategy comes with the potential to generate a significant alpha but on the flip side it comes with a high risk.
One needs to evaluate their risk profile and choose an investment portfolio according to their goals and risk bearing capacity. Thus it is best to do your own due diligence and decide whether Momentum strategy suits one’s style of investing.
Visit our Knowledge Center for more articles on Samco Mutual Funds. You can also find many valuable blogs in our Help and Support section.
